When you truly understand Blockchain Technology its intrinsic value is evident and its inevitable place in our future is obvious.
The Purpose Of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain Technology has the potential to disrupt or replace whole industries especially current professions and institutions that have operational models based on trust or being intermediaries. For example, banks, estate agents, insurance companies, custodians, lawyers, solicitors, courts, and record labels to name a few. This is because Blockchain Technology has the capabilities to provide accounting, security, authentication, secure decentralised records, trustworthiness, reliability, and anonymity to name a few.
These services are usually provided by third parties like those mentioned in the previous paragraph. These services are costly and usually increase regularly. The Blockchain can and does provide these services at a fraction of the price and unlike traditional institutions the system has built in incentives to decrease prices rather than increase them.
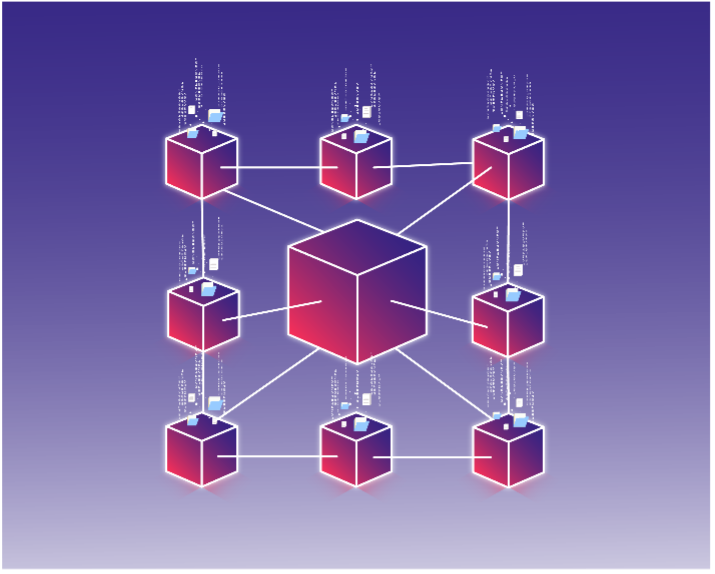
How The Blockchain Works
Think of Blockchain technology as a decentralised digital ledger to store information. Each block has limited storage capacity, once a block is filled it is added to a chain of previously formed blocks. The information stored on a Blockchain is chronologically ordered and cannot be altered. Therefore, a Blockchain is a reliable source of information and ideal for recording asset transactions. All transactions are crossed referenced with all previous blocks and all the computers on the network which have identical records. This process is completely automated and immune to human error.
Example 1
To illustrate the real-world potential of the Blockchain let’s look at the conventional process of a house purchase as an example. Let’s say you’re selling your house, for the purpose of trust you are required/expected to utilise the services of a lawyer, estate agents, a bank, and the county court. All at a substantial cost. Using these services gives both the buyer and the seller peace of mind the transaction will be legitimately executed. However, the same transaction can be executed on the Blockchain with the same guarantees that give both the buyer and seller their desired peace of mind.

Example 2
Another example to further demonstrate Blockchain technologies inevitable place in our future lives are Smart Contracts. A simple explanation to aid understanding of the Blockchains Smart Contract utility is travel. Let’s say you were travelling from the UK to Jamaica on an 8-hour flight that leaves at 12pm in the afternoon and arrives at 8pm in the evening (GMT). If there were any delays to take off, mealtimes and arrival, you are in theory entitled to a partial refund. However, receiving this refund requires a lot of time, effort and negotiations with several customer service departments who have the tendency to redirect you elsewhere. Now imagine you completed the same journey but this time you paid with the Cryptocurrency Ethereum (Cryptocurrencies are another utility of Blockchain Technology). Amazingly if there were delays this time you refund would be credited into your account automatically and immediately. There would be no need for the time-consuming labour-intensive rigmarole many of us have experienced.
The Future Of Blockchain Technology
Slowly but surely more and more innovative uses for Blockchain Technology will be created. Solving problems, making our lives easier and entertaining us. And like its predecessor the internet Blockchain Technology will surreptitiously integrate into our lives until one day suddenly it is indispensable.
10 Easily Digestible Bullet Points About Blockchain Technology
- A more self-explanatory name for a Blockchain is a Public Digital Ledger. Sealed with transactions, titles and deeds.
- A collection of data accurately collated with secure decentralised storage.
- A set amount of data is authenticated by computers. The authenticated data forms a block and is added to previously formed blocks creating a chain, hence Blockchain.
- The data consists of digital currency and asset transactions, as well as smart contracts.
- There is no centralised authority. The Blockchain data is securely stored on computers all over the world (decentralised).
- Anyone can join and become a verifier on a Blockchain (this is known as mining). All the incorruptible data ever added to the Blockchain can be viewed by anyone.
- To function the Blockchain is dependant on cryptology and the internet (peer-to-peer network).
- So far some of the uses for Blockchain Technology include Cryptocurrency, NFTs, Smart Contracts, Games and Gambling to name a few.
- Different cryptocurrencies have separate Blockchains for example, Bitcoin and Ethereum have their own Blockchains.
- With a Blockchain there is no central point for failure or single point for attack by hackers.